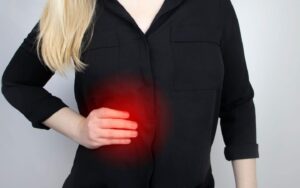
If you’ve injured your ribs while playing a sport like rugby or football before, you’ll know that it can be both uncomfortable and unpleasant! It’s important to seek proper care to reduce your risk of complications. Read on to find out how physiotherapy could help with your recovery.
Anatomy of the rib cage
The rib cage, or thoracic cage, is made up of 12 thoracic vertebrae, 12 pairs of ribs (lightweight, curved bones), intercostal muscles, cartilage, and the sternum. The thoracic cage provides stability and support for the upper body, protects vital organs including the lungs and heart, and aids breathing. It also acts as an attachment point for muscles in the upper body.
What are the common symptoms of rib pain?
Symptoms of rib injuries range from mild discomfort that resolves in several days to severe pain that takes weeks or months to heal. Common symptoms include: a sharp or dull pain in the chest that worsens when breathing in, sore and tender ribs that may be accompanied by bruising, and a popping or cracking sound if a fracture occurs.
It’s important to seek emergency medical treatment if you experience severe pain or pressure in the chest and breathing difficulties, as this could indicate a medical emergency, such as a heart attack.
What are the common causes?
The most common causes of rib pain include:
- Bruised or strained intercostal muscles
- Broken or fractured ribs
- Sports injuries
- Trauma from motor vehicle accidents or falls
- Severe coughing during illness
- Stiffness in spine overloading the thoracic cage
- Rib subluxation or slipped rib syndrome
- Osteoporosis (increasing chances of fracture)
- Inflamed rib cartilage, known as costochondritis (inflammation of the cartilage connecting the rib to the sternum).
Can rib pain be managed at home?
If you’re experiencing a mild to moderate muscle strain, you may be able to take some steps at home to manage your symptoms.
- Breathe normally and deeply to clear your lungs and avoid chest infections
- Use over-the-counter medication to manage the pain, as advised by your Doctor
- Avoid sports or exercises that aggravate the pain
- Use ice therapy to reduce any swelling
- Holding a pillow to your chest for support if you need to cough or sneeze
- Try to remain upright as much as possible, and prop yourself up to sleep
- Avoid straining or lifting heavy objects
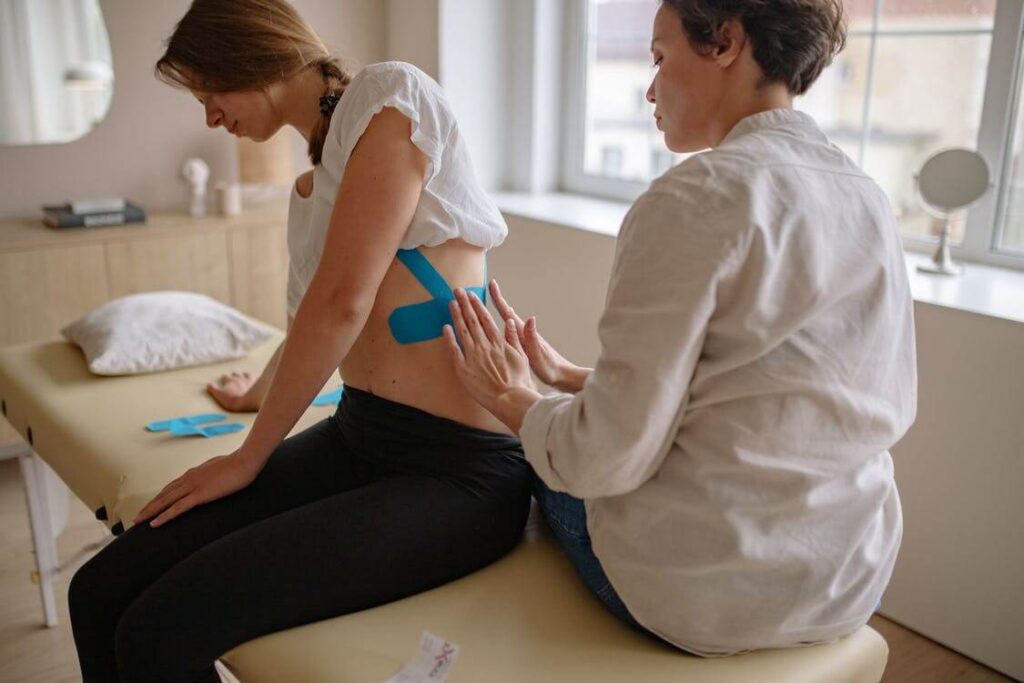
How can physiotherapy help?
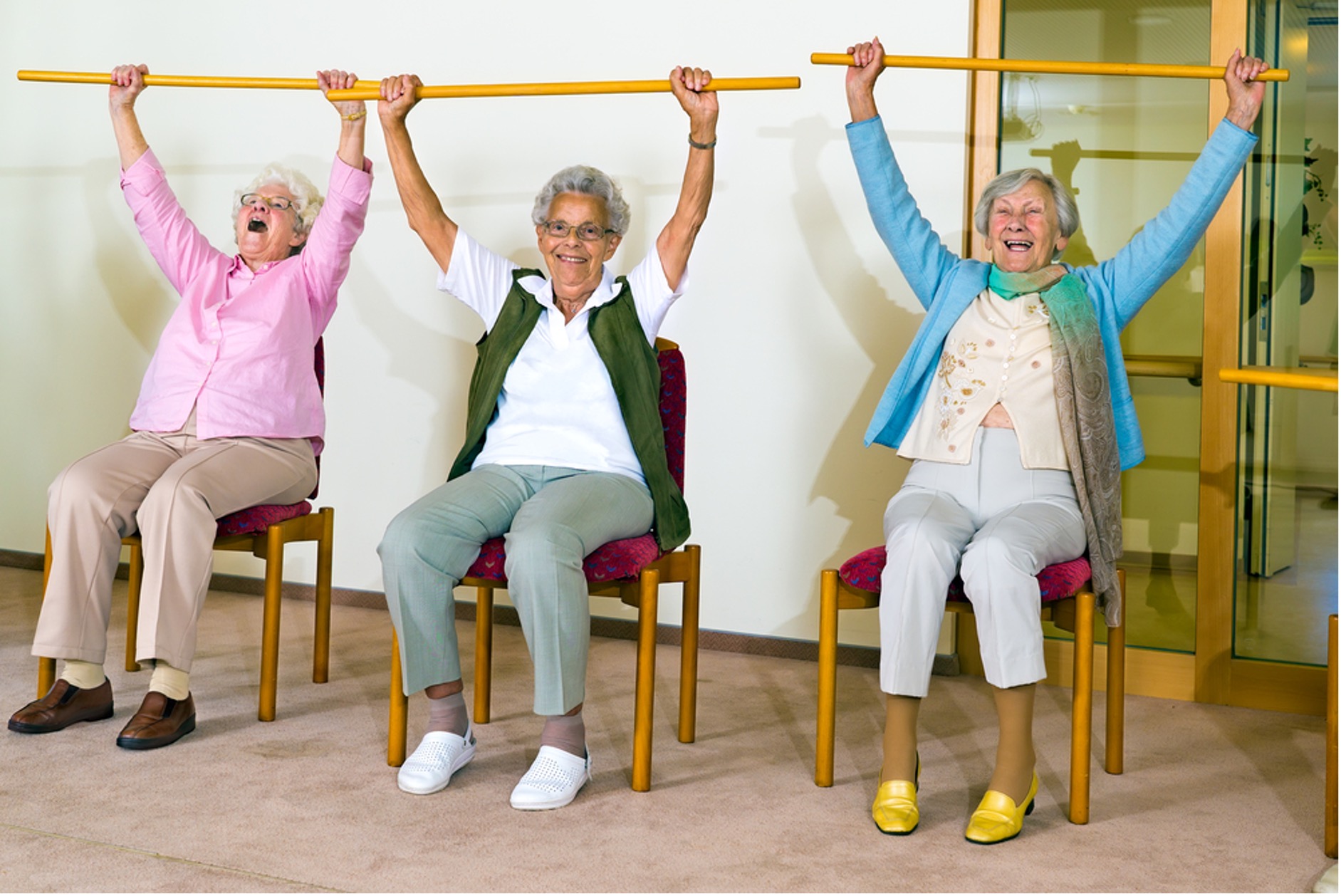
Physiotherapy aims to restore your normal range of motion and function. It could be an important part of your recovery from a rib injury. Treatment may involve breathing exercises and chest stretches performed slowly and gradually. If you’ve suffered a fracture or cracked rib, make sure you get medical clearance from your GP before commencing exercise.
As physios, we work with you to understand the cause of your symptoms and come up with an appropriate plan for treatment. We can show you the proper technique for stretches and exercises to ease your discomfort and promote recovery. We can also provide advice on how to manage your injury at home.
Deep breathing for broken ribs
Deep breathing is essential to prevent chest infections or pneumonia. A gentle breathing exercise you can start with is to sit upright in a chair or a bed. Hold a pillow over your chest for support then breathe slowly and deeply until your lungs are full. Try to hold your breath for up to ten seconds, then slowly exhale. Repeat five times, several times a day.
If you need help managing your symptoms, come and see us. Give us a call on (08) 9203 7771 or email info@ngp.net.au to make an appointment, and we’ll get you back to your best!
References:
- Physio-pedia (2020). [Online]. Available at: https://www.physio-pedia.com/Ribs (Accessed 20 July 2022).
- (2019). What causes rib pain and how to treat it. [Online]. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/rib-cage-pain (Accessed 20 July 2022).
- NHS (2021).Broken or bruised ribs. [Online]. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/broken-or-bruised-ribs/ (Accessed 20 July 2022).
- WebMD (2020). Best exercises for broken ribs recovery. [Online]. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/best-exercises-broken-ribs-recovery (Accessed 20 July 2022).